In the world of finance, Understanding Cumulative Abnormal Return (CAR) is essential for investors and analysts seeking insights into stock or portfolio performance. The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) measures the difference between the expected return of a stock (or portfolio) based on a benchmark and its actual return over a specific period. Investors use it to assess how well a stock has performed relative to market expectations, providing critical insights for investment decisions.
In this article, we’ll explore the key components of cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR), its significance in finance, and how it’s applied in various scenarios. We will also examine the concept of abnormal returns and provide examples of how they are calculated and used in the financial world.
What is Cumulative Abnormal Return?
Cumulative Abnormal Return (CAR) refers to the total difference between the actual returns of an asset and its expected returns over a specific period. The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) is particularly useful for analyzing how events, such as corporate earnings announcements or regulatory changes, affect a stock’s performance beyond normal market fluctuations.
In essence, it helps investors measure the performance deviation of a stock from its expected trajectory, providing valuable insights into whether a stock has over or underperformed in comparison to the market.
Key Takeaways
- Cumulative Abnormal Return (CAR) helps gauge stock performance relative to market expectations.
- The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) is widely used by investors and financial analysts.
- Positive CAR indicates outperformance, while negative CAR suggests underperformance.
What is Cumulative Abnormal Return Used For?
Investors utilize Cumulative Abnormal Return to analyze how particular events or decisions have affected the stock or portfolio’s return. This metric is crucial during events like mergers, acquisitions, earnings reports, or any significant corporate action. The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) helps assess whether these events have had a positive or negative impact on stock performance compared to the benchmark.
For instance, if a company releases a positive earnings report, investors would expect the stock price to rise. If the stock’s return surpasses market expectations, the CAR will show a positive abnormal return.
Abnormal Return: Definition, Causes, Example
Abnormal Return refers to the deviation between the actual return of a stock or portfolio and its expected return based on a benchmark, such as an index like the S&P 500. The causes of abnormal returns can vary widely, from market news, economic reports, and corporate actions to unexpected events like regulatory changes.
Example of Abnormal Returns
Let’s consider a scenario where an investor buys a stock that is expected to yield an 8% return based on market trends. If the stock actually returns 12%, the abnormal return is 4%. This 4% is the unexpected gain or “abnormal return.”
The Significance of Cumulative Abnormal Return in Finance
Cumulative Abnormal Return (CAR) is a crucial tool in financial analysis, helping investors and analysts understand how specific events have impacted a company’s stock. For example, an earnings report may affect investor sentiment, leading to a stock price surge or decline. The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) helps measure the extent of this impact.
For investment managers, CAR is essential for portfolio performance evaluation. It highlights how well a portfolio manager has performed compared to market expectations, providing a performance metric beyond simple returns.
What is Abnormal Return?
Abnormal Return is defined as the difference between the actual return of an asset and its expected return based on market forecasts. The abnormal return is a key performance metric used to evaluate the success of investment strategies. It helps investors understand whether the returns achieved were due to skillful investment decisions or simply market movements.
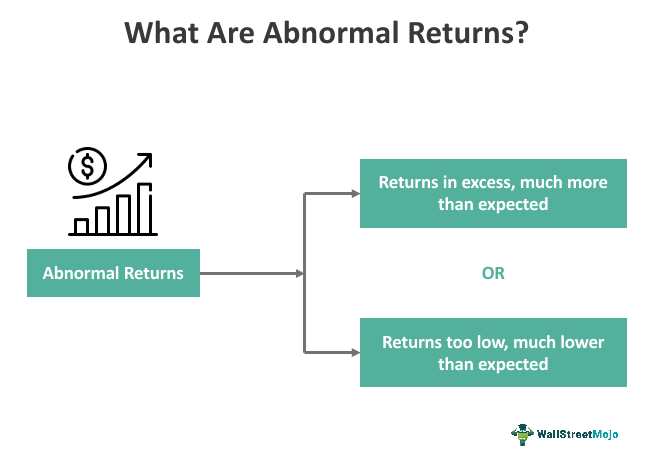
Abnormal returns can be both positive and negative. Positive abnormal returns suggest that the investment has outperformed market expectations, while negative abnormal returns indicate underperformance.
Abnormal Return Explained
The abnormal return metric is essential for evaluating the performance of portfolio managers and investment strategies. It gauges whether their stock selection and market predictions have produced better-than-expected results or fallen short.
If a portfolio consistently generates positive abnormal returns, it indicates that the manager’s investment decisions are successful. However, if the abnormal return is negative, it suggests poor performance compared to the market.
Formula for Abnormal Return
To calculate abnormal return, the formula is:
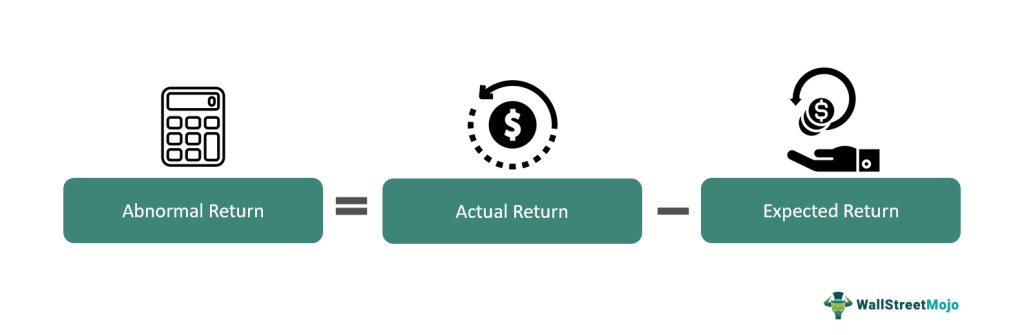
Abnormal Return=Actual Return−Expected Return\text{Abnormal Return} = \text{Actual Return} – \text{Expected Return}Abnormal Return=Actual Return−Expected Return
Where the expected return can be determined using the
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM): Er= Rf+β(Rm−Rf)Er = Rf + β (Rm – Rf)Er=Rf+β(Rm−Rf)
Where:
- Er = Expected return
- Rf = Risk-free rate
- β = Beta (volatility of the security compared to the market)
- Rm = Return on the market (benchmark index)
Example of Abnormal Returns
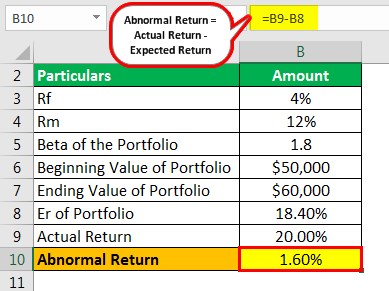
Suppose a portfolio has a beginning value of $50,000 and an ending value of $60,000. Using the CAPM model, we calculate the expected return to be 18.40%. The actual return of the portfolio is 20%. Using the abnormal return formula:

Example 1
Let’s say you have the following data:
- Risk-free rate (RfR_fRf): 4%
- Market return (RmR_mRm): 12%
- Beta (β\betaβ): 1.5
- Actual return: 20%
Step 1: Calculate Expected Return
Using the CAPM formula:
Expected Return=4%+1.5×(12%−4%)=4%+1.5×8%=4%+12%=16%
Step 2: Calculate Abnormal Return:
Abnormal Return=Actual Return−Expected Return=20%−16%=4%
Here, the abnormal return is 4%, indicating that the investment outperformed expectations by 4%.
Example 2:
Consider a scenario where a company announces a new product, and the stock’s performance is evaluated:
- Risk-free rate (RfR_fRf): 3%
- Market return (RmR_mRm): 10%
- Beta (β\betaβ): 0.8
- Actual return: 8%

Step 1: Calculate Expected Return
Expected Return=3%+0.8×(10%−3%)=3%+0.8×7%=3%+5.6%=8.6%
Step 2: Calculate Abnormal Return
Abnormal Return=Actual Return−Expected Return=8%−8.6%=−0.6%
In this case, the abnormal return is -0.6%, indicating that the stock underperformed expectations by 0.6%.
Importance of Abnormal Return in Finance
- Performance Metric: Abnormal return helps evaluate the performance of portfolio managers.
- Event Analysis: Helps understand how external events like mergers or earnings reports impact stock prices.
- Investment Strategy: A crucial measure to assess whether a stock’s performance is driven by market forces or investment decisions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How to find cumulative abnormal return?
To find cumulative abnormal return (CAR), you calculate the abnormal return for each period and sum them over the desired timeframe.
2. What is the meaning of cumulative return?
Cumulative return refers to the total return on an investment over a specific period, including both gains and losses.
3. How to calculate cumulative abnormal return (CAR)?
The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) is done by summing the abnormal returns across multiple periods.
4. What is the meaning of abnormal return?
Abnormal return is the difference between the actual return of an asset and its expected return based on market expectations.
5. What is meant by cumulative abnormal return?
Cumulative abnormal return (CAR) is the sum of abnormal returns over a set period, helping to analyze how events impact stock performance.
6. Can cumulative abnormal return be negative?
Yes, cumulative abnormal return can be negative if the stock or portfolio underperforms compared to expectations.
Conclusion
Understanding Cumulative Abnormal Return (CAR) is essential for evaluating investment performance. The cumulative abnormal return calculation (CAR) provides key insights into how a stock or portfolio reacts to market events, enabling investors to make more informed decisions. By measuring deviations from expected returns, investors can assess whether their strategies are working or require adjustments.