1-Understanding I/O Drawers:
If you’ve come here to learn about I/O drawers and how they can enhance data flow in your systems, you’re in the right place! This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about I/O drawers, explaining their benefits in simple and easy-to-understand language.
So, what exactly are I/O drawers? An I/O drawer, short for Input/Output drawer, is a specialized component used in computer systems to manage and organize multiple input and output devices. Think of it as a dedicated space within a computer or server where various I/O devices, such as storage drives, network cards, and other peripherals, are connected and managed efficiently.
I/O drawers play a crucial role in enhancing data flow and system performance. By organizing and centralizing I/O devices, these drawers help reduce data bottlenecks, improve processing speed, and ensure smoother communication between different parts of your computer system. They are particularly valuable in environments that require high data throughput, such as data centers, large enterprises, and high-performance computing setups.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the components of I/O drawers, how they work, and the numerous advantages they offer. We will also explore practical applications, installation tips, and future trends in I/O drawer technology. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an IT professional, or just curious about how to boost your system’s efficiency, this guide will provide you with all the information you need.
Table of Contents
2-Key Components of I/O Drawers:
Welcome back! Now that we’ve got a basic understanding of what I/O drawers are, let’s dive into their key components. Knowing what makes up an I/O drawer will help you appreciate how they enhance data flow and system performance.

An I/O drawer typically consists of several essential components:
- Controller Card: The controller card acts as the brain of the I/O drawer. It manages the communication between the connected I/O devices and the main system. This card ensures that data is transferred efficiently, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall system performance.
- Expansion Slots: These are the slots where you plug in various I/O devices like storage drives, network cards, and other peripherals. The expansion slots are designed to accommodate a range of devices, allowing for flexible and scalable system configurations.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The power supply unit provides the necessary power to all the connected I/O devices. A reliable PSU ensures that your devices operate smoothly without any interruptions, which is crucial for maintaining high data throughput.
- Cooling System: Efficient cooling is vital for the optimal performance of an I/O drawer. The cooling system, which may include fans or liquid cooling solutions, helps to dissipate heat generated by the I/O devices. Keeping temperatures in check prevents overheating and ensures longevity and reliability of your hardware.
- Connectivity Ports: These ports facilitate the connection between the I/O drawer and the main system. Common types of connectivity ports include USB, Thunderbolt, and PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express). These high-speed ports ensure fast data transfer rates, enhancing the overall efficiency of your setup.
- Enclosure: The physical casing or enclosure of the I/O drawer protects all internal components from dust, physical damage, and electromagnetic interference. A well-designed enclosure not only provides protection but also helps in organizing the I/O devices neatly.
3-How I/O Drawers Work:
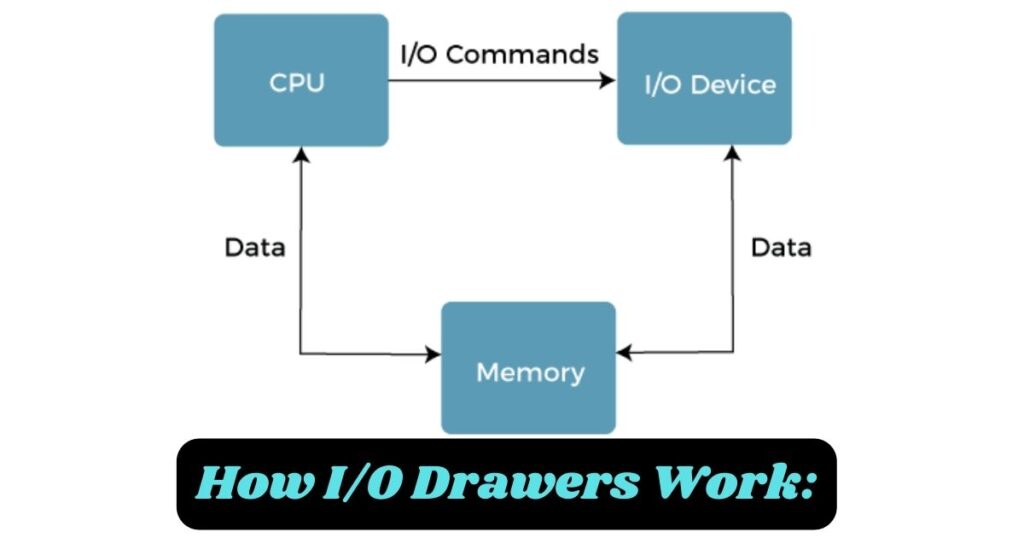
Welcome back! Now that we’ve covered the key components of I/O drawers, let’s explore how these components come together to enhance your system’s performance. Understanding how I/O drawers work will help you appreciate their benefits even more.
I/O drawers are designed to manage the flow of data between your computer’s main system and its various peripheral devices. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
- Data Input: When you use an input device like a keyboard, mouse, or storage device, it sends data signals to the I/O drawer. For example, when you type a document, your keyboard inputs data into the system.
- Data Processing: The controller card in the I/O drawer takes these input signals and processes them. It decides the best way to route this data to the appropriate part of the computer system. This step is crucial for maintaining smooth and efficient data flow.
- Data Transfer: After processing, the data is transferred from the I/O drawer to the main computer system via connectivity ports like USB, Thunderbolt, or PCIe. These high-speed connections ensure that data moves quickly and without delay.
- Data Output: Once the main system processes the data, it sends output signals back to the I/O drawer. This output could be anything from displaying text on a monitor to printing a document. The I/O drawer routes these signals to the correct output devices.
- Feedback Loop: The process of input, processing, transfer, and output happens continuously and rapidly, creating a seamless feedback loop. This loop allows for real-time interaction with your computer system, whether you are typing, gaming, or managing data.
- Resource Management: I/O drawers are also responsible for managing system resources efficiently. They ensure that data transfers do not overload the system, thus preventing bottlenecks. For instance, if you are transferring large files to an external hard drive while streaming a video, the I/O drawer manages these tasks simultaneously without causing delays.
- Cooling and Power Management: As data is transferred and processed, the components in the I/O drawer generate heat. The cooling system works to dissipate this heat, ensuring the devices operate within safe temperature ranges. Meanwhile, the power supply unit ensures all components receive consistent power, maintaining stability and performance.

By centralizing the management of input and output devices, I/O drawers streamline data flow and reduce the strain on the main computer system. This results in faster data processing, improved performance, and greater flexibility in system configurations.
4-Benefits of Using I/O Drawers:

Welcome back! Now that you have a solid understanding of how I/O drawers work, let’s dive into the benefits of using them. I/O drawers can significantly enhance your computing experience in several ways:
- Enhanced Performance: I/O drawers optimize data flow between your computer and its peripheral devices. By managing data transfers efficiently, they reduce bottlenecks and improve overall system performance. This is especially beneficial for tasks that require high-speed data transfer, such as video editing, gaming, and large file transfers.
- Improved Scalability: One of the standout benefits of I/O drawers is their ability to scale. As your computing needs grow, you can add more devices without overloading your system. This is particularly useful for businesses or individuals who frequently upgrade their hardware or add new peripherals.
- Better Resource Management: I/O drawers manage system resources effectively, ensuring that tasks are prioritized and handled without causing delays. This results in smoother multitasking and more efficient use of your computer’s processing power and memory.
- Increased Flexibility: With multiple connectivity options like USB, Thunderbolt, and PCIe, I/O drawers offer great flexibility. You can connect a wide range of input and output devices, from keyboards and mice to high-speed storage drives and advanced graphics cards.
- Enhanced Cooling and Power Efficiency: I/O drawers often come with built-in cooling systems and power management features. These ensure that your devices operate within safe temperature ranges and receive consistent power, preventing overheating and system instability.
- Simplified Cable Management: By centralizing connections in one place, I/O drawers help reduce cable clutter. This not only makes your workspace neater but also simplifies the process of connecting and disconnecting devices.
- Improved Reliability: I/O drawers are designed to handle high volumes of data transfer and processing. They are built with robust components that enhance the reliability and longevity of your system.
By leveraging these benefits, I/O drawers can transform your computing setup, making it more powerful, efficient, and versatile. Whether you’re a professional working with data-intensive applications or a casual user looking for a smoother computing experience, I/O drawers offer tangible advantages that enhance everyday use.
5-Choosing the Right I/O Drawer for Your Needs:
Selecting the right I/O drawer is crucial to maximize its benefits. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an I/O drawer for your system:
- Compatibility: Ensure the I/O drawer is compatible with your computer system and operating system. Check the available ports and connections to match your existing hardware.
- Connectivity Options: Look for an I/O drawer with multiple connectivity options such as USB, Thunderbolt, and PCIe. This will provide flexibility to connect a variety of devices.
- Performance Specifications: Consider the data transfer speeds supported by the I/O drawer. Higher speeds are essential for tasks that require rapid data movement, such as video editing or gaming.
- Cooling System: Check if the I/O drawer has an efficient cooling system to manage heat generated during operation. This is important for maintaining optimal performance and preventing overheating.
- Power Management: Ensure the I/O drawer has reliable power management features to provide consistent power to connected devices and prevent power surges or drops.
- Scalability: If you anticipate needing more peripherals in the future, choose an I/O drawer that supports expansion. This will allow you to add more devices without needing a complete overhaul of your system.
- Build Quality and Reliability: Invest in an I/O drawer built with high-quality components. This ensures durability and reliable performance over time.
- Budget: While it’s tempting to go for the most feature-rich option, consider your budget. Look for an I/O drawer that offers the best balance of features and affordability.
- User Reviews and Recommendations: Research user reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources. Real-world experiences can provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of the I/O drawer you’re considering.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose an I/O drawer that perfectly matches your needs, enhancing your system’s performance and efficiency. Whether you’re upgrading your current setup or building a new one, the right I/O drawer can make a significant difference in your computing experience.
6-Best Practices for Using I/O Drawers:
Welcome back! In this section, we’ll explore some best practices for using an I/O drawer effectively. Following these tips will help you maximize the performance and longevity of your I/O drawer.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your I/O drawer and connected devices clean and dust-free. Dust can accumulate and cause overheating or connectivity issues. Use compressed air to clean ports and connectors periodically.
- Update Firmware and Drivers: Manufacturers often release firmware and driver updates for I/O drawers to improve performance and fix bugs. Regularly check for updates and install them to ensure your I/O drawer is running optimally.
- Proper Cable Management: Organize cables neatly to avoid tangling and ensure easy access to ports. Use cable ties or organizers to keep cables in place. This not only keeps your workspace tidy but also prevents wear and tear on cables and connectors.
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring tools to keep an eye on the performance of your I/O drawer. Check for any signs of overheating, data transfer slowdowns, or connectivity issues. Early detection of problems can prevent major issues down the line.
- Optimal Placement: Place your I/O drawer in a well-ventilated area to ensure proper airflow. Avoid placing it in enclosed spaces where heat can build up. Adequate ventilation helps maintain optimal temperatures and prevents overheating.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all cables and connectors are securely plugged into the I/O drawer. Loose connections can lead to data transfer errors or device malfunctions. Double-check connections whenever you add or remove devices.
- Use High-Quality Cables: Invest in high-quality cables that support the data transfer speeds and power requirements of your devices. Cheap or substandard cables can cause performance issues and may not provide adequate power to connected devices.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not overload your I/O drawer with more devices than it can handle. Check the specifications to understand the maximum number of devices it supports and the power requirements. Overloading can lead to performance degradation and hardware failures.
- Backup Data Regularly: Regularly back up data from devices connected to your I/O drawer. This ensures that you don’t lose important information in case of hardware failure or data corruption.
- Seek Professional Help: If you encounter persistent issues with your I/O drawer, seek professional help. A technician can diagnose and fix complex problems that you might not be able to resolve on your own.
7-Future Trends in I/O Drawer Technology:
The world of technology is always evolving, and I/O drawers are no exception. Here are some future trends that are set to transform the way we use I/O drawers:
- Increased Data Transfer Speeds: As demand for faster data transfer grows, future I/O drawers will support even higher speeds. Technologies like USB 4.0 and Thunderbolt 4 will become more common, allowing for quicker data transfers and improved performance.
- Enhanced Wireless Connectivity: Wireless technology is rapidly advancing. Future I/O drawers may incorporate advanced wireless standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2, reducing the need for cables and providing more flexibility in device placement and connectivity.
- Integration with Smart Devices: The integration of I/O drawers with smart home and office devices is on the horizon. This will allow for seamless control and management of various devices through centralized systems, making workflows more efficient.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies will likely be incorporated into I/O drawers to optimize performance. These technologies can analyze usage patterns and adjust settings automatically to enhance efficiency and reliability.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Future I/O drawers will focus on energy efficiency, incorporating features that reduce power consumption without compromising performance. This is crucial for sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of technology.
- Modular Designs: Modular I/O drawers that allow for easy upgrades and customization will become more prevalent. Users will be able to add or remove components based on their needs, providing greater flexibility and scalability.
- Enhanced Security Features: As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, future I/O drawers will include advanced security features to protect data and devices. This might include built-in encryption, secure boot processes, and real-time threat detection.
- Smaller Form Factors: Advances in technology will lead to smaller, more compact I/O drawers without sacrificing performance. This will make it easier to integrate them into various setups, from home offices to large data centers.
- Cloud Integration: Integration with cloud services will become more seamless, allowing for easier data synchronization and remote management. This will enable users to access their devices and data from anywhere, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
8-Optimizing I/O Drawer Performance:
Welcome to the next section, where we’ll delve into optimizing the performance of your I/O drawer. By following these tips, you can ensure that your I/O drawer operates at its best, providing seamless connectivity and efficient data transfer.
- Update Firmware and Drivers Regularly: Keep your I/O drawer’s firmware and drivers up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest hardware and software updates. Manufacturers often release patches and enhancements that improve performance and address compatibility issues.
- Optimize Device Placement: Place high-speed devices closer to the I/O drawer to minimize cable length and signal degradation. This reduces latency and ensures optimal performance for devices that require rapid data transfer, such as external SSDs or graphics cards.
- Utilize High-Speed Ports: Take advantage of high-speed ports like Thunderbolt or USB 3.1 for devices that require fast data transfer rates. These ports offer significantly higher bandwidth compared to standard USB ports, allowing for quicker file transfers and reduced lag.
- Enable Hardware Acceleration: Many modern I/O drawers support hardware acceleration features for tasks like video encoding or rendering. Enabling hardware acceleration offloads processing tasks from the CPU to specialized hardware, resulting in faster performance and smoother playback.
- Optimize Cable Management: Proper cable management is essential for maintaining optimal signal integrity and airflow. Use high-quality cables of the appropriate length and avoid excessive bending or twisting, which can cause signal loss or damage to connectors.
- Monitor Temperature and Cooling: Keep an eye on the temperature of your I/O drawer and connected devices, especially during heavy usage. Excessive heat can degrade performance and reduce the lifespan of components. Ensure adequate airflow and consider adding additional cooling solutions if necessary.
- Manage Power Consumption: Configure power-saving settings for devices connected to your I/O drawer to minimize energy consumption when idle. This not only reduces your environmental footprint but also helps prolong the lifespan of your hardware.
- By implementing these optimization techniques, you can unlock the full potential of your I/O drawer and create a high-performance computing environment tailored to your needs.
9-Troubleshooting Common I/O Drawer Issues:
Despite their benefits, I/O drawers may encounter issues from time to time. In this section, we’ll explore some common issues and how to troubleshoot them effectively.
- Connection Problems: If devices connected to your I/O drawer are not recognized or fail to function properly, check the cable connections and ensure they are securely plugged in. Try using different cables or ports to rule out connectivity issues.
- Slow Data Transfer: Slow data transfer speeds can be caused by various factors, including outdated drivers, insufficient bandwidth, or hardware limitations. Update your drivers, optimize your network settings, and consider upgrading to faster storage or connectivity options if necessary.
- Device Compatibility Issues: Ensure that your devices are compatible with your I/O drawer and the ports you are using. Some devices may require specific drivers or firmware updates to function correctly.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause performance degradation and hardware failures. Ensure proper ventilation and cooling for your I/O drawer and connected devices. Clean any dust or debris from fans and vents regularly to maintain optimal airflow.
- Interference: Nearby electronic devices or electromagnetic interference can disrupt signals and cause connectivity issues. Move your I/O drawer away from sources of interference and use shielded cables to minimize signal degradation.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicting software or drivers can cause instability or performance issues. Update your operating system and drivers to the latest versions, and consider disabling unnecessary background processes or applications that may be consuming resources.
- Hardware Failures: If you suspect a hardware failure, perform diagnostic tests or consult with a technician for further assistance. Components such as cables, connectors, or the I/O drawer itself may need to be replaced if they are found to be faulty.
- Firmware Corruption: In rare cases, firmware corruption can occur, causing devices to malfunction or become unresponsive. Resetting the firmware to factory defaults or updating it to the latest version may resolve the issue.
- Network Connectivity Problems: If your I/O drawer is connected to a network, ensure that your network settings are configured correctly and that your router or switch is functioning properly. Check for network congestion or bandwidth limitations that may affect performance.
10-Expanding Connectivity: Harnessing the Power of I/O Drawers for Enhanced Device Integration:
In this section, we’ll explore how I/O drawers can expand connectivity options, allowing for seamless integration of a wide range of devices into your computing environment.
Utilizing Expansion Slots for Device Expansion
I/O drawers often feature multiple expansion slots, allowing you to add additional connectivity options to your system. Whether you need extra USB ports, additional network interfaces, or specialized expansion cards for audio, video, or storage, expansion slots provide the flexibility to tailor your setup to your specific requirements.
By strategically selecting and installing expansion cards in your I/O drawer, you can customize your system to support a diverse range of devices and peripherals. This enables you to optimize your workflow and maximize productivity by seamlessly integrating all the tools and resources you need.
Supporting Multi-Device Connectivity with I/O Drawer Hubs
I/O drawers equipped with built-in hubs offer a convenient solution for managing multiple devices simultaneously. These hubs provide additional ports and connectors, allowing you to connect multiple peripherals such as external hard drives, printers, cameras, and more to your system with ease.
With the ability to connect multiple devices to a single I/O drawer hub, you can streamline your workspace and reduce cable clutter. This simplifies connectivity and enhances productivity by eliminating the need for multiple adapters and hubs scattered across your desk.
Enhancing Data Transfer Speeds with High-Speed Interfaces
Many modern I/O drawers feature high-speed interfaces such as Thunderbolt, USB 3.0, or PCIe, offering blazing-fast data transfer speeds and low latency connectivity. These interfaces enable rapid communication between your system and connected devices, allowing for seamless data transfer and real-time interaction.
By harnessing the power of high-speed interfaces, you can significantly reduce transfer times and improve overall system performance. Whether you’re transferring large files, streaming high-definition media, or running demanding applications, high-speed interfaces ensure smooth and efficient operation
11-Installation and Setup of I/O Drawers:
In this section, we’ll guide you through the process of installing and setting up I/O drawers, ensuring seamless integration into your computing environment.
Understanding I/O Drawer Components
Before proceeding with installation, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the components of an I/O drawer. These typically include expansion slots for connecting additional devices, built-in hubs for managing multiple peripherals, and high-speed interfaces such as Thunderbolt or USB 3.0 for fast data transfer.
Physical Installation of I/O Drawers
Begin by identifying an appropriate location for your I/O drawer, ensuring easy access to your computer’s ports and connectors. Next, securely mount the drawer in place, following the manufacturer’s instructions and using the provided mounting hardware. Ensure that all cables and connectors are properly routed to avoid interference and maintain a tidy workspace.
Connecting Devices to the I/O Drawer
Once the drawer is securely installed, it’s time to connect your devices. Utilize the expansion slots to add additional connectivity options, such as USB ports, network interfaces, or specialized expansion cards. Ensure that each device is securely seated in its respective slot and properly aligned for optimal performance.
Configuring Device Settings
After connecting your devices, you may need to configure their settings to ensure compatibility with your system. This may involve installing device drivers, adjusting configuration settings, or updating firmware as necessary. Refer to the documentation provided with each device for detailed instructions on configuration and setup.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Once installation and setup are complete, it’s essential to test the functionality of your I/O drawer and connected devices. Verify that all devices are recognized by your system and functioning correctly. If any issues arise, refer to the troubleshooting section of the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance on resolving common problems.
Conclusion:
I/O drawers serve as pivotal components in modern computing environments, offering versatile solutions for expanding connectivity options and seamlessly integrating a diverse array of devices. By leveraging expansion slots, users can tailor their systems to accommodate specific needs, whether it involves adding extra USB ports, network interfaces, or specialized expansion cards. This flexibility empowers users to optimize their workflows, enhancing productivity and efficiency in various tasks.
Moreover, the integration of built-in hubs in I/O drawers simplifies multi-device connectivity, streamlining workspaces and reducing cable clutter. With the convenience of centralized connectivity, users can effortlessly manage multiple peripherals, such as external hard drives, printers, and cameras, from a single hub. Additionally, the adoption of high-speed interfaces like Thunderbolt and USB 3.0 enables rapid data transfer and real-time interaction, further augmenting system performance. Overall, I/O drawers represent essential tools for enhancing device integration and connectivity in computing environments, facilitating seamless operation and unlocking new possibilities for users.



















1 Comment
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.livebetdu.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m extremely impressed with your writing talents as smartly
as with the structure in your weblog. Is
that this a paid subject or did you modify it yourself?
Either way keep up the excellent high quality writing, it’s uncommon to see a great blog like this one nowadays.
Stan Store alternatives!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m really impressed together with your writing skills and also with the layout for your blog.
Is that this a paid topic or did you modify it your self?
Either way stay up the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to peer a great
weblog like this one nowadays. Beehiiv!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
70918248
References:
least harmful steroid
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
70918248
References:
best online steroid suppliers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Don’t bounce the burden off the floor or you’ll find
a way to end up lifting with dangerous form. Even though they’re each deadlifts variations the setup, execution and
muscular tissues activated are completely different. As you’re
training, start with lighter weights, and use progressive
overload to build up over time. As A Outcome Of the Romanian is
effective with a decrease weight, this is a superb
option for a home gym.
Few issues in the gym are as satisfying as selecting heavy weights up off the
floor. Apart from being a deeply satisfying feeling, deadlifts are additionally a highly functional exercise.
As such, training this motion sample might help
scale back aches and pains experienced with day by day actions whereas making you a stronger, more physically capable human in on a regular basis life.
These are only some of the a quantity of advantages of performing
deadlifts as a half of your coaching routine.
Each Romanian deadlifts and lunges are useful exercises for building a robust
and sculpted decrease physique.
For the usual RDL, you want to start standing
erect, holding the bar with a double-overhand grip. When going heavy, you might use a mixed grip, however I recommend sticking with a double overhand grip throughout
your lighter sets to build up your grip strength.
One option for getting into the RDL starting place is to deadlift the.Romanian deadlift strength
requirements assist you to to check your one-rep max raise with other lifters at
your body weight. Unlike the Romanian deadlift, the deadlift is a raise that serves itself,
typically the usual expression of maximal pulling
power.
Deadlifts are usually your heaviest lift and a compound motion that makes use of many alternative muscle teams.
Subsequently, by incorporating deadlifts into your training program, you may gain extra
lean muscle mass when performed correctly. One of one of the best benefits of deadlifts, is the entire body power they’ll produce.
Deadlifts are a compound motion, meaning they use a quantity
of muscle groups, joints and stabilizing muscle tissue, in unison, providing you with more bang
on your buck in phrases of constructing more power.
The Romanian deadlift (RDL) is a lesser-known variation of the basic deadlift, which strengthens the glutes and hamstrings.
Whereas the RDL and the Deadlift have their unique advantages, it’s worth considering incorporating both workout routines into your coaching routine.
By doing so, you can reap the advantages of every exercise and luxuriate in a well-rounded leg-strengthening program.
One Other crucial factor to consider when choosing between the RDL and the Deadlift is your individual biomechanics and limitations.
Deadlifts are completely different to different workout routines like the bench press or squat the place the load starts on the prime.
The deadlift motion begins from the bottom and and you pull the weight up then return it to the floor for one rep.
One of the most typical causes for damage whereas deadlifting is rounding
the back.
When it involves strength training workouts, the deadlift and Romanian deadlift are two in style selections that
target the posterior chain and provide numerous advantages.
Whereas each workout routines contain lifting weights from the ground,
they differ by way of method, muscle activation, and overall coaching
goals. The deadlift is the king of exercises in phrases of building strength and muscle mass all
through the entire body, therefore the rationale you
see it incorporated into so many various workout applications.
On the other hand, the Romanian Deadlift is a variation that locations a
higher emphasis on the hamstrings and glutes.
It is executed by hinging at the hips with a slight bend in the knees, lowering the barbell down the shins to only beneath knee degree, after
which driving by way of the heels to return to the beginning position.
When you compare standard deadlifts and Romanian deadlifts, you would possibly notice that one seems easier
than the other. For most movers who are just
starting out on the gym, the Romanian deadlift is going to
be the primary deadlift you ever work on. It is a great place
for engaged on maintaining a flat back, building hamstring power, and studying tips on how to carry out a hip
hinge. To carry out the deadlift correctly, one should start by
standing with the feet shoulder-width apart and the barbell centered over the midfoot.
The lifter should bend on the hips and knees,
preserving the again straight and the chest lifted.
In this text, we’ll break down the necessary thing differences
between these two types of deadlifts, explore their advantages, and guide you thru proper technique to maximise your features.
By understanding the difference between the Romanian deadlift and deadlift, you’ll
find a way to resolve which one is finest suited to
your health objectives. The Romanian deadlift is
barely completely different than the traditional deadlift.
Although both movements will improve strength
and produce greater muscle hypertrophy in the posterior chain muscular tissues, Romanian deadlifts put extra emphasis on the hamstrings, versus the glutes [R].
Perhaps one of the efficient exercises, the deadlift is a tried-and-true compound functional motion that’s utilized to construct full body
power for extra explosiveness, pace, and energy. The deadlift, much
like many other resistance training workouts, comes with many variations which embody the Romanian deadlift, straight leg deadlift,
and the sumo deadlift.
References:
the understanding gender is permanent is called
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
G. Stand up before returning the burden again to the starting place.
Once you are feeling assured with the movement, try this
15-minute CrossFit partner workout, which options the
dumbbell snatch. E. When the barbell brushes towards mid-thighs, drive hips forward (allowing toes to leave
the ground).
Wodstar has not disappointed…there are such a lot of daily workouts
to choose from! I use their Lean Program, lost weight, and am positively fitter…remodeling fat into lean muscle mass!
Catch the barbell with your thighs above parallel (hip crease above your
knees).
The snatch is probably certainly one of the most complex Olympic weightlifting movements.
It can additionally be one of the most effective exercises
for creating explosive power. Once you nail the power
snatch broken down above, you’ll find a
way to attempt the barbell squat snatch. For the squat
snatch, quite than catching the barbell overhead along with your
legs in a quarter squat, you’ll catch it in the bottom of your squat,
and then press the bar overhead whilst you stand up.
Good CrossFit coaches will assist you to with method and the method to modify the exercise for the Workout of the Day.
Rogue IWF Accredited Olympic Weightlifting Bar – when you want a real, dedicated Olympic lifting bar,
you won’t be the quality or value of this one. It is obtainable in both 28mm and 25mm shaft diameters, designed for male and female competitors.
Wrap your first two or three fingers over your thumbs and pin your thumb between your fingers and the barbell.
This offers you a stronger grip while also stopping the bar from slipping out
of your arms. Programming the snatch depends on many
elements, together with an athlete’s needs, proximity to competitors, program focus, periodization, and age of the athlete.
I love the combination between operating, swimming, and Crossfit-style coaching.
From this conventional power snatch, we can start tweaking
it and dealing on different methods and strategies that can be utilized
to shave seconds from WOD occasions. The traditional strategy to the Oly lifts is
to use these movements to develop explosive pace and power.
They have certainly been confirmed effective for that function, and the most effective results are found with shorter sets.
CrossFitters are certainly interested in explosive energy and
speed and will practice low-rep Oly lifts. However true general physical preparedness (GPP)
requires that we not pursue them to the exclusion of the opposite domains of health.
Including high-rep snatch (and clean) exercises has a broader
goal than training only power and pace. The snatch is certainly one of the two lifts contested in Olympic weightlifting, the
opposite being the clean and jerk.
You might also find that you simply’re better at one or the other, so you may
naturally gravitate towards your strengths.
These gold standard lifts are essential to a well-rounded routine.
This Is tips on how to prioritize when you do not have time for both.
Once you’re a master snatcher and able to try out the
break up snatch, watch this CrossFit break up snatch video.
C. Grip the bell with an overhand grip, then shift hips up towards the ceiling so that chest is over
the weight.
The snatch should be a staple in your program if you wish to improve efficiency in any sport or your overall health.
The snatch variation that you will see most often in CrossFit?
“You can energy snatch or squat snatch a barbell,” says Milgram.
Discover out the method to do basically any of the snatches workout
strikes you will encounter in CrossFit, together with energy snatches,
squat snatches, and break up snatches with
barbells, dumbbells, and kettlebells. Working your way backwards through
the snatch can beextremely helpful (think of negative pull ups!).
If you battle with the catchpositions, then drill overhead squats and snatch balances.
If your problemarea is transitioning from beneath the knee to above the knee, try engaged on a hang snatch below the knee or a pause
snatch, these might help yourbody and thoughts to connect the 2 movements.
Below, you will study the advantages of all the snatches workout
strikes — plus how to do each snatch CrossFit variation you see in all those WODs.
We have already talked about the importance of mobility,but it is so necessary if
you want to work in path of a strong snatch that itdeserved a second mention. For
a great snatch you MUST be ready to squat to therequired depth with strong type and also you
MUST have the flexibility to maintain the bar (in thesnatch
grip) overhead along with your lats activated. Another great drill to work on is the three-positionsnatch – the ability place (bar on the hips), the grasp place (above theknees) and a full
snatch from the ground. To full the repetition, drive your heels throughthe flooring and stand up.
If you’ve a small window of time in the gym but you need to get better
at both workouts, prioritize the squat.
The squat trains the identical muscular tissues
you employ in the deadlift, but via a larger range of movement, in accordance with Samuel.
The strength you construct in a squat will carry over into the deadlift.
The same might be true for carryover from a deadlift to a squat,
however not to the same extent. If your aim is to improve athleticism, the deadlift strengthens muscle tissue
that work in the hip extension mechanics that energy movements like operating and
leaping. In the muscle snatch, the lifter lifts the bar all the way overhead
with arms locked out and the hip and knee totally extended.
The snatch is amongst the two movements judged in competitive weightlifting.
Athletes can receive large bodily and psychological rewards for grinding by way of the motion and doing what’s prescribed, and 30 squat snatches at 135 lb.
The squat snatch is a rewarding but challenging
train that can take your training to new heights.
By following this guide and training persistently,
you’ll build the strength, power, and coordination needed to perform
this spectacular movement with confidence and precision.
References:
Steroids Effect On Body
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
That being said, attempt discovering an elite-level powerlifter with small biceps.
The goal of a powerlifting competition is to raise the heaviest amount of weight possible in one
or all three of these lifts. The barbell squat additionally stimulates the
entire physique, from the muscle tissue across the hips and knees performing the movement to the
trunk, ankles, shoulders, and arms stabilizing.
We’re a staff of dedicated lifters, and this is the place where we nerd
out about powerlifting approach. Our sources embrace skilled teaching,
on-demand powerlifting programs, and in-depth articles.
Honestly – one of the best all spherical internet hosting gyms we have and you may be welcomed no matter your degree.
In 2023 they hosted a offered out and fun meet which
allowed visitors to come into their prized health club.
We have been extremely proud to have the ability to host at this venue
with nice parking and loads of room. If weighing in on the
day of competing, weigh in is 8 to 8.30am. Day earlier than lifting 24 hour weigh in – 10am
to 11am OR 5-6pm. Huge occasion area, a lot of parking and tea/coffee/water on sale by way of the day.
Sarah Bradley, the hostess with the mostess is back for 2024!
Each jurisdiction will have totally different necessities to compete at this degree, which may include having competed in numerous
native competitions or reaching a qualification standard.
There could also be extra individuals in your age and weight class at this degree
to compete in opposition to. Power Ambassadors is devoted
to providing a top-tier group setting for powerlifting, Olympic
weightlifting, and strongman training. With skilled coaches and a welcoming group, we provide every little thing you have to obtain your goals safely and confidently.
Turning Into a member of Powerlifting America grants
you access to premier competitions, unique assets, and a supportive
neighborhood of fellow lifters dedicated to the game. Powerlifting consists of
three completely different lifts – a squat, deadlift and a bench press.
After two phases of making ready the joints, connective
tissues, and muscle tissue, there’s a deload week earlier than the final phase
of powerlifting exercises. The first program is for those
new to the massive three lifts and heavier power coaching generally.
The purpose the large three lifts are used in powerlifting
is as a result of they use the highest variety of muscle teams, working simultaneously
to move probably the most weight possible. Nevertheless, a powerlifting program may
be beneficial for the general population. In a full powerlifting meet, opponents get three attempts
at each carry, to provide the very best complete attainable.
This article incorporates plenty of useful information, suggestions, and proposals for those
thinking about powerlifting coaching.
Whereas it is a goal for all people who carry weights, for powerlifters,
it’s particularly top-of-mind due to the sheer amount of weight
they’re lifting. Worldwide there are a number of powerlifting federations
that govern the sport. Every federation has slightly completely different technical rules, weigh-in protocols, and policies around drug testing.
Whether Or Not you’re a beginner trying to build confidence
with weights or a seasoned lifter coaching on your
next competitors, our gym supplies a welcoming space for all.
The time spent recovering far outstrips the time spent within the
fitness center. Even if you’re more targeted on basic well-being or getting a seashore body, a
powerlifting program can actually be part of your overall method.
While muscle hypertrophy, conditioning, and suppleness are all essential components, the central focus of a powerlifting program is increasing your one-repetition maximum (1RM).
The goal of the bench press is just to unrack the burden, lower it to the
chest, and lock out the arms at the top. The powerlifting bench press recruits not solely
the chest, shoulders, and triceps however the whole upper and lower again, hips, and legs.
Some embrace maximal attempts at all three lifts while
others specialize in one or two on a given day.
This depends on the person seeking to start
a powerlifting routine. Form is something that rapidly gets forgotten about as weights increase, leading to unhealthy habits, and sadly,
many coaching accidents. Outdoors of the gym, some people battle to stick
to their rest days between workouts. The risk of damage
is highest when making an attempt to carry maximal weights.
They are used to running novice entry level competitions and now have a wealth of skilled
lifters who prepare and compete there. Anybody that can safely carry out the squat, bench press, and deadlift can use a powerlifting program.
Plus, working a newbie powerlifting program can really assist you to improve coordination and motor recruitment.
This is a 15 week intermediate powerlifting program from PRs on the Platform.
It utilizes block periodization and could be run repeatedly or used to peak for a powerlifting competitors.
As a volunteer, you’ll be at the coronary heart
of the action, assisting with important duties such as setting up tools,
managing logistics, and making certain the graceful operation of the event.
Miss Churchyard, who trains at Fortitude Fitness in Ipswich and competes within the lighter weight categories, said from early on she found herself always coming again to push
herself further. The now 21-year-old has been given the
nickname “Tiny Tank” due to her small posture
and high power, in addition to for her success
in the sport. We are anticipating a lot more data
soon for the Europeans so please keep watching.
This is why you have to treat your first competition as a studying experience more than anything.
What you have to notice is that the primary competition is not
essentially about ‘testing your power’, however quite, studying what the competition setting appears and looks
like. There are many to choose from, however my
favorite is the Titan Yellow Jacket Knee Sleeves (check sizing and at present’s price).
Check out my complete guide on the Best Powerlifting Singlets.
I tested and reviewed 5 of the most popular manufacturers available on the market.
In the Usa, the IPF affiliate is USA Powerlifting,
which has a presence in all 50 states.
I can’t tell you what number of occasions I see new athletes on game-day with out the proper help, and aren’t in a place
to translate their energy successfully on the competitions platform.
There are no shortages of powerlifting programs on the internet.
My objective with this article is to provide the most informative content about tips on how to begin powerlifting, grow your strength, and find success in competition. The level of powerlifting is to raise as much
weight as attainable for 1 repetition within the squat, bench press, and deadlift.
Powerlifting rules are starting to be used in older populations that are at danger of dropping their strength and mobility.
Over time, a number of specialized types of weightlifting
have turn out to be well-liked sports activities in their very own proper.
This in style sport includes strikes derived from powerlifting, Olympic lifting,
strongman, and extra. Exercises encompass a “WOD” or workout of the day that everyone in the gym participates in with modifications to accommodate differing ability ranges.
Olympic lifters usually start with these derivative lifts to work on the skills and power wanted
to carry out the two primary lifts concerned within the sport.
Ryan Stinn shared with us the significance of focusing on high
quality technique, and never sacrificing your kind to try to carry heavier weights.
This is a lifter who has competed in 15 National Championships, so he undoubtedly knows how to prioritize longevity in the sport.
Please fill out the contact type supplied and a member of our employees will reach out to you.
At UK Powerlifting United, your safety is what’s most important to us.
All enquires will be handled very seriously, with the utmost discretion.
Remember – you will need a present 2025 membership
FOR THAT yr you may be competing AT WEIGH IN.
Remember – you will need a present membership FOR THAT year you’re competing AT WEIGH IN.
Bear In Mind – you will want a current 2024 membership FOR THAT yr you might be competing
AT WEIGH IN. Keep In Mind – you will want a present
membership FOR THAT yr you are competing AT
WEIGH IN. When you compete with the UK IPL,
when you check our qualifying totals and discover you
have hit one of them and wish to compete then please contact
us on for your invitation. The UK IPL do ship us their results but
some of the lifters we don’t have contact particulars
for, so please reach out.
Powerlifting is a very specific sport, with a simple aim – to get as strong as possible.
Extra advanced lifters will have the flexibility to steadily progress in depth on the big three whereas adding accent workout routines to convey up any weak elements of their
lifts. The lifts have to be accomplished with strict rules round kind, with three judges scoring every
try. The deadlift is a true present of maximal strength and is often the heaviest lift in a powerlifter’s arsenal.
Thanks to PRs on the Platform for sharing this program
with Lift Vault through the program submission type.
If you want to crush PRs, add slabs of muscle, or lose weight, KIZEN has the perfect program for you.
Most federations are represented, including USAPL, USPA, APF, PA, SPF, OPW, and RPS.
It’s not your average health program, contemplating
lengthy restoration occasions aren’t optionally available.
However as we’ve realized, it’s one of the best ways to get greater.
Their exercises concentrate on quality and maximal
effort quite than dozens of workouts and lightweight weights.
A powerlifting program will in fact be centered around the huge three lifts, with different exercises taking half in important
supplementary roles. The greatest advantage of going via a powerlifting program is
clearly the features in your maximal power. When beginning a
powerlifting program, be ready to prioritize relaxation and restoration, each inside and outside the gym.
The results of powerlifting coaching are totally different from the typical DOMS seen in bodybuilding or
general health programs. Powerlifting training may be carried out by people of various experience ranges, although it will look totally different for
every particular person. It includes pushing yourself to lift heavy weights persistently, and with glorious method.
You won’t find many pump-up units of bicep curls in a powerlifting program.
Kyle Risley based Lift Vault in 2016 to make discovering great powerlifting applications simpler.
Since then, the location has grown to include hundreds
of programs for energy, bodybuilding, Olympic weightlifting, and extra.
He at present lives in Massachusetts and continues to compete in powerlifting.
It’s frequent to see athletes of their 50s and 60s competing of their first competitors.
How you carry out the squat, bench press,
and deadlift as a powerlifter will be a lot different than if
you’re a bodybuilder. This is as a result of powerlifters wish to reduce the vary of motion as
much as possible for every carry. They additionally
wish to use each muscle in the body when executing the
motion.
It’s used to develop lure and grip power, as properly as become accustomed to bracing the core
for heavy deadlifts. The close-grip bench press will target
the triceps more effectively, bringing them up to scratch when making an attempt heavy
bench numbers. This is the exercise of the big three that permits the lifting of essentially the most total weight and recruits the whole
body to do so. Improving your maximal energy
will translate properly to other coaching metrics, whether
or not or not it’s muscle development, velocity, or cardio power.
Although it could feel embarrassing to go back to
fundamentals and strip down to lighter weights, it’s crucial to your long-term success to get out of your head and train accurately.
Unfortunately, this leads to injuries in powerlifting, particularly within the
decrease again, shoulders, and knees.
In competitions, they have three tries to successfully lift a pre-chosen amount of weight utilizing each
lift. Do Not worry about chopping weight for your first competitors anyways.
Just compete at no matter bodyweight you stroll round normally, even when that is
in between two lessons. Let’s now speak about competing within the sport of powerlifting
– how you must mentally method it, how to register, and suggestions for game day.
Over time, lots of lifters will have specific squat
footwear and deadlift footwear. Check out my article on how robust you
should be at your first powerlifting meet.
Here are a few of my prime tips for powerlifting
technique when you’re getting began.
Many powerlifters start in their 30s and 40s and compete well into their 50s.
Because you compete in an age class, you would possibly be solely ranked
relative to your given age bracket. With that mentioned, powerlifting does have
illustration within the Para-Olympic Games, the place lower-body disabled athletes compete within the bench press.
The bench press has been a Para-Olympic sport for men since 1964
and for ladies since 2000. In powerlifting, the
goal isn’t essentially to isolate a person muscle group while performing
the squat, bench press, or deadlift.
You will at all times feel such as you’re not sturdy or prepared enough.
My favorite is the Economy Lever Belt from LiftingLarge.com (check sizing and at present’s price).
Lifting belts should follow sure specs to put on in competition, and this one meets these criteria.
There isn’t any shortage of powerlifting gear that you could get your arms on.
In single lifts the bench solely limitless class can be included.
Adam Hindle and the team are back running our qualifiers for the
South West Salisbury and the equipped mecca that is
349 Barbell. The unimaginable staff consists of
some of largest and greatest equipped lifters within the country (certainly
biggest……) and includes a few of the highest
ladies. The group embrace rivals within the prime tier
WPO Superfinals and the ABS Pro collection so you would
possibly be in amazing hands. The major variables manipulated in a powerlifting program
are frequency, depth, and quantity.
I wrote a complete article on how to change from a bodybuilding program to a powerlifting program.
Any powerlifting federation (including USA Powerlifting) that you simply compete in may have certain requirements for each of the lifts.
As we age, we lose muscle mass at a sooner rate than earlier in life.
Primarily Based on getting older studies, it’s estimated that we lose
8% of muscle mass each decade after the age of 40.
High-intensity strength training, like powerlifting, has been shown to
decelerate this process.
References:
https://shsportsclub.com/what-is-gua-sha-why-you-need-this-facial-treatment-how-to-make-it-at-home/
https://www.selfhackathon.com/when-to-start-post-cycle-therapy/
https://niazshomal.ir/city/babol/author/darlaebg31/
https://www.selfhackathon.com/does-gua-sha-really-work-to-minimize-a-double-chin/
http://www.ardenneweb.eu/archive?body_value=%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Ch1%3EYou+Can%27t+Gua+Sha+Away+A+Double+Chin%3C/h1%3E%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Ch2%3EYou+Can%27t+Gua+Sha+Away+a+Double+Chin%3C/h2%3E%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++Gua+Sha%2C+the+traditional+Chinese+healing+technique+involving+the+scraping+of+skin%2C+is+often+touted+for+its+ability+to+improve+circulation+and+treat+various+health+issues.+But+one+thing+it+can%27t+do%3F+Reduce+the+appearance+of+a+double+chin.++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++A+double+chin%2C+characterized+by+excess+fat+in+the+lower+jaw+area%2C+is+primarily+influenced+by+genetics%2C+aging%2C+or+weight+gain+leading+to+loose+skin.+While+Gua+Sha+may+help+reduce+puffiness+or+improve+skin+texture%2C+it+doesn%27t+target+fat+accumulation.++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++For+those+considering+Gua+Sha+as+a+solution%2C+it%27s+important+to+understand+its+limitations.+It+works+best+for+minor+adjustments+and+can+complement+other+treatments%2C+but+it+won%E2%80%99t+eliminate+a+double+chin+on+its+own.+If+you%27re+looking+for+more+significant+changes%2C+consider+facial+exercises%2C+surgery%2C+or+lifestyle+modifications+like+maintaining+a+healthy+weight+and+staying+hydrated.++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++In+conclusion%2C+while+Gua+Sha+offers+benefits+for+facial+health%2C+don%27t+rely+solely+on+it+to+reduce+a+double+chin.+Pairing+it+with+a+holistic+approach+yields+the+best+results.%3Cbr%3E+%3Cbr%3E++Sources:+%3Ca+href%3D%22https://jbhnews.com%22%3ELearn+More%3C/a%3E+.
https://holisticdoggie.com/uncategorized/9-top-steroids-without-side-effects-legal-and-safe/
https://heealthy.com/question/strengthen-your-jawline-effective-exercises-for-men-women/
https://www.89u89.com/author/rodrigokoni/
https://community.orbitonline.com/users/georgiannamckim/
https://avicounsel.com/evaluating-treatment-outcomes-for-hypogonadal-men-with-intramuscular-testosterone-cypionate-versus-subcutaneous-testosterone-enanthate/
https://www.escortskart.com/user/profile/ErickLenk22
https://www.pallapattipickr.com.tr/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=673
https://www.ekursu.com/index.php?qa=7191&qa_1=the-ultimate-human-growth-hormone-guide
https://tsopedu.org/blog/index.php?entryid=38376
https://ethiofarmers.com/post-cycle-therapy-what-is-pct-and-is-it-necessary/
https://haloleagues.com/how-to-hydrate-your-skin-3-simple-methods-as-recommended-by-experts/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
[…] and engage their target audience. But what exactly is outstream video advertising(What Is Outstream Video Advertising), and how does it differ from other forms of online advertising? In this comprehensive guide, […]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[…] “Enhancing Data Flow: Exploring the Benefits of I/O Drawers”: […]